Explore by checking out the first article from each issue. If you're interested in discovering more about an issue, click to view the complete Table of Contents to see what each issue has to offer.
Prostate Biopsy: Targeting Cancer for Detection and Therapy
Technology Update
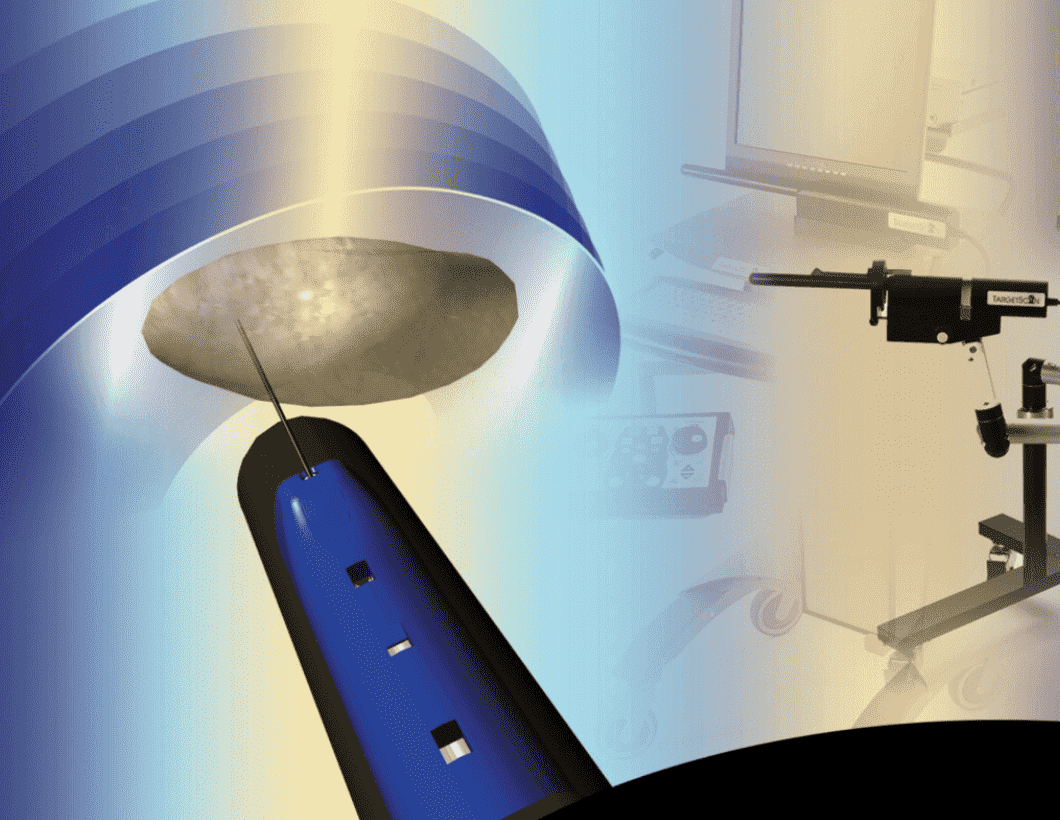
Despite improvements in cancer detection, prostate biopsy still lacks the ability to accurately map locations of cancer within the prostate. Improvements in prostate imaging may allow more accurate mapping of overall disease volume. Magnetic resonance (MR) spectroscopy allows improved specificity in detecting even small foci of disease within the peripheral zone. Improvements in MR-guided biopsy techniques may allow this technology to be adapted to therapeutics as well. Computer modeling of individual prostates serves as a means of designing optimized plans for prostate biopsy. The use of novel targeted biopsy schemes may allow an integration of available technologies in detection and localization of prostate cancer. Computer-directed needle biopsies based on anatomic landmarks within the prostate and computerized three-dimensional reconstruction of the gland may allow a highly reproducible means of identifying small foci of cancer, targeting them for therapy, and monitoring for recurrence. The TargetScan® system (Envisioneering Medical Technologies, St. Louis, MO) is the first technology to integrate available targeting methodologies in a systematic fashion. [Rev Urol. 2006;8(4):173-182]
Management of Overactive Bladder With Transdermal Oxybutynin
Treatment Update
Roger R DmochowskiJonathan S Starkman
In clinical trials, transdermal oxybutynin (OXY-TDS) has shown comparable efficacy and improved tolerability when compared with conventional pharmacotherapy. Systemic anticholinergic adverse effects are comparable to those with placebo, most likely owing to avoidance of first-pass hepatic metabolism and conversion of oxybutynin to N-desethyloxybutynin. OXY-TDS has predictable pharmacokinetic absorption and elimination parameters, as shown in both in vitro and in vivo studies. Consistent plasma concentrations of oxybutynin avoid labile peak and trough concentrations seen with immediaterelease formulations, paralleling extended-release drug delivery. This novel drug delivery system has unique dermatologic skin application site reactions, including erythema and pruritus. Skin reactions are usually mild and can be minimized by varying the site of patch application. Most eczematous dermatologic reactions can be appropriately treated with a moderately potent topical corticosteroid cream. A small percentage of patients will discontinue therapy as a result of bothersome application site skin reactions. [Rev Urol. 2006;8(3):93-103]
Overactive bladderTolterodineAnticholinergic medicationsOxybutinin
Erectile Function Outcomes in the Current Era of Anatomic Nerve-Sparing Radical Prostatectomy
Therapeutic Challenges
The contemporary use of anatomic nerve-sparing radical prostatectomy, which entails preserving the autonomic nerve supply to the penis required for penile erection, has led to improved erectile function outcomes compared with what has been seen historically. However, delay of postoperative recovery of erection for as long as 2 years is common, such that dysfunctional erection status lingers as a major postoperative problem. Several possible strategies to improve overall recovery rates and to hasten postoperative recovery of erectile function are currently being advanced. These include pharmacologic rehabilitation therapy and neuromodulatory therapy. Rigorous basic scientific investigation and clinical assessment of these new strategic approaches are critically important to establish their actual therapeutic benefits. [Rev Urol. 2006;8(2):47-53]
Prostate cancerRadical prostatectomyErectile dysfunctionNeuromodulationPenile erection