Unlike non–muscle invasive bladder cancer, which can be treated with surgical and intravesical medication administration, upper tract urothelial (renal pelvis and ureter) cancer was historically treated only surgically. If a tumor could not be treated with ureteroscopic or percutaneous surgical control, removal of the kidney and ureter was often the only treatment option. When mitomycin for pyelocalyceal instillation 0.4% gel for low-grade upper urothelial cancer became commercially available, nonsurgical treatment became possible.
Mitomycin for pyelocalyceal instillation 0.4% gel can be instilled via a retrograde approach (through a ureter catheter placed from the bladder or externally up into the ureter and renal pelvis) or an antegrade approach (through a nephrostomy tube). The drug can be administered in the office, ambulatory surgery center (ASC), or hospital outpatient department (HOPD). Because of these variations in route of administration, it is vital to understand the appropriate reporting of these services for accurate reimbursement.
The recommended schedule is to instill mitomycin for pyelocalyceal instillation 0.4% gel once weekly for 6 weeks. It may also be administered once a month for a maximum of 11 additional instillations.
Volumetric Determination Before Therapy
Before the first instillation of the drug, volumetric determination of the renal pelvis volume is necessary to determine the amount of gel to be instilled, regardless of the drug administration approach. Coding for the volumetric study is site dependent and typically takes place at the same time as the initial instillation of the drug.
For volumetric determination, the health care professional reports the Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) code based on the documented approach, which includes 1 of the following:
- For the antegrade procedure through a nephrostomy tube:
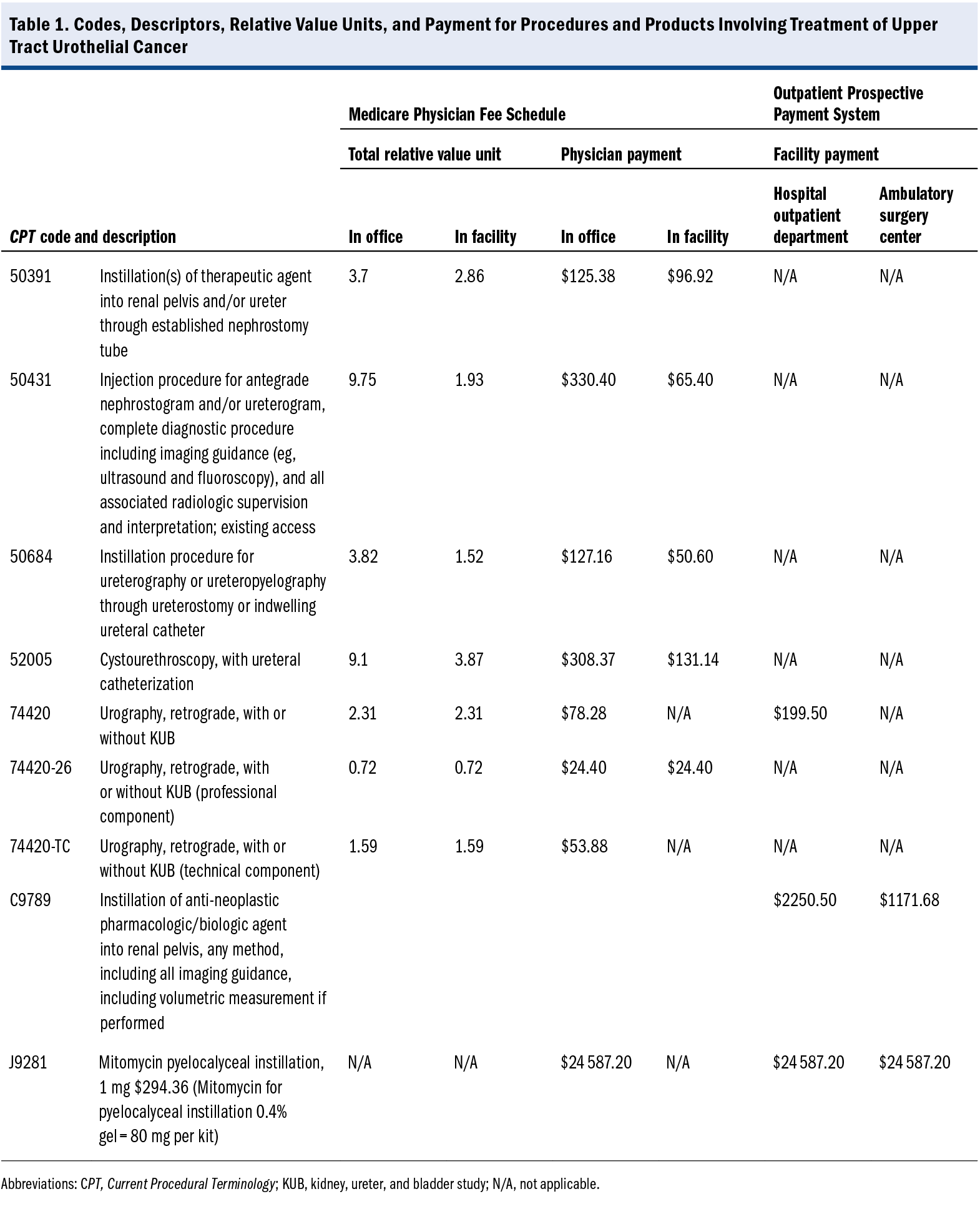
50431 Injection procedure for antegrade nephrostogram and/or ureterogram, complete diagnostic procedure including imaging guidance (eg, ultrasound and fluoroscopy), and all associated radiologic supervision and interpretation; existing access - For the retrograde procedure with cystoscopy and ureter catheter placement:
52005 Cystourethroscopy, with ureteral catheterization, with or without irrigation, instillation, or ureteropyelography, exclusive of radiologic service - For the retrograde procedure with an externalized ureter catheter:
50684 Instillation procedure for ureterography or ureteropyelography through ureterostomy or indwelling ureteral catheter
In addition, an interpretation CPT code would be reported for interpretation of the test:
- For the antegrade procedure:
74425 Urography, antegrade, radiological supervision and interpretation - For any retrograde procedure:
74420 Urography, retrograde, with or without KUB [kidney, ureter, and bladder study]
Notes:
- If one is billing for CPT 74420 or 74425, a separate paragraph within the operative report or separate report should be documented, which includes a description of the procedure, how it was performed, the volume injected, and the description of findings.
- If performing the procedure at an ASC or HOPD, the health care professional should append modifier 26 (Professional service) for the interpretation; the facility would report the same code using the technical component modifier.
The ASC would also report code 77420 or 74425, if provided, because the status of the code under the Hospital Outpatient Prospective Payment System is Z2, and it is allowed if it is integral to the service provided on the same date.
Note: The volumetric determination is typically performed just once, meaning that CPT code 74420 or 74425 would not be reported with each instillation but reported again only if there is a medically necessary reason to repeat the volumetric determination.
Abbreviations
ASC ambulatory surgery center
CPT Current Procedural Terminology
HOPD hospital outpatient department
Medication Administration
The appropriate CPT code to report for administration of the gel itself is based on the instillation approach.
For retrograde instillation of gel performed with cystoscopy and ureter catheter placement, the following CPT code should be documented and reported:
- 52005 Cystourethroscopy, with ureteral catheterization, with or without irrigation, instillation, or ureteropyelography, exclusive of radiologic service
For retrograde instillation of gel performed through an externalized ureter catheter, the following CPT code should be documented and reported:
- 50684 Instillation procedure for ureterography or ureteropyelography through ureterostomy or indwelling ureteral catheter
For antegrade instillation of gel through a previously placed nephrostomy tube, the following CPT code should be documented and reported:
- 50391 Instillation(s) of therapeutic agent into renal pelvis and/or ureter through established nephrostomy, pyelostomy or ureterostomy tube (eg, anticarcinogenic or antifungal agent)
Note: These instillation codes are all 0-day global procedures, meaning that any associated evaluation and management service is included and not reported or reimbursed separately. An evaluation and management service on the same day as an instillation should be billed only if a separate and identifiable service is performed and documented.
Regardless of the place of service (office, ASC, or HOPD), the supply of mitomycin for pyelocalyceal instillation 0.4% gel should also be reported by the entity purchasing the drug. For the office, mitomycin for pyelocalyceal instillation 0.4% gel would be reported on the physician billing form in conjunction with the appropriate CPT code based on the method of instillation and the volumetric study, if performed. For the ASC or HOPD, the facility would typically report the mitomycin for pyelocalyceal instillation 0.4% gel with the appropriate approach or pass-through code and the volumetric study code, if required and provided.
Note: It is important to report the mitomycin for pyelocalyceal instillation 0.4% gel administered; J code J9281 (Mitomycin pyelocalyceal instillation, 1 mg) is the correct code. The number of units administered is also required to correctly code the instillation of the drug.
Notes About the Currently Available Preparation of Mitomycin for Pyelocalyceal Instillation
The product is a reverse thermal hydrogel technology that is a liquid when cool (when it can be instilled), and then turns into a gel when reaching body temperature. It is sold in a kit with two 40-mg vials. When the mitomycin for pyelocalyceal instillation gel is prepared for treatment of a patient, it is a liquid and measured in milliliters. The concentration of mitomycin for pyelocalyceal instillation is 4 mg per 1 mL of gel. For each treatment, the physician will determine the amount of mitomycin for pyelocalyceal instillation gel to be instilled.
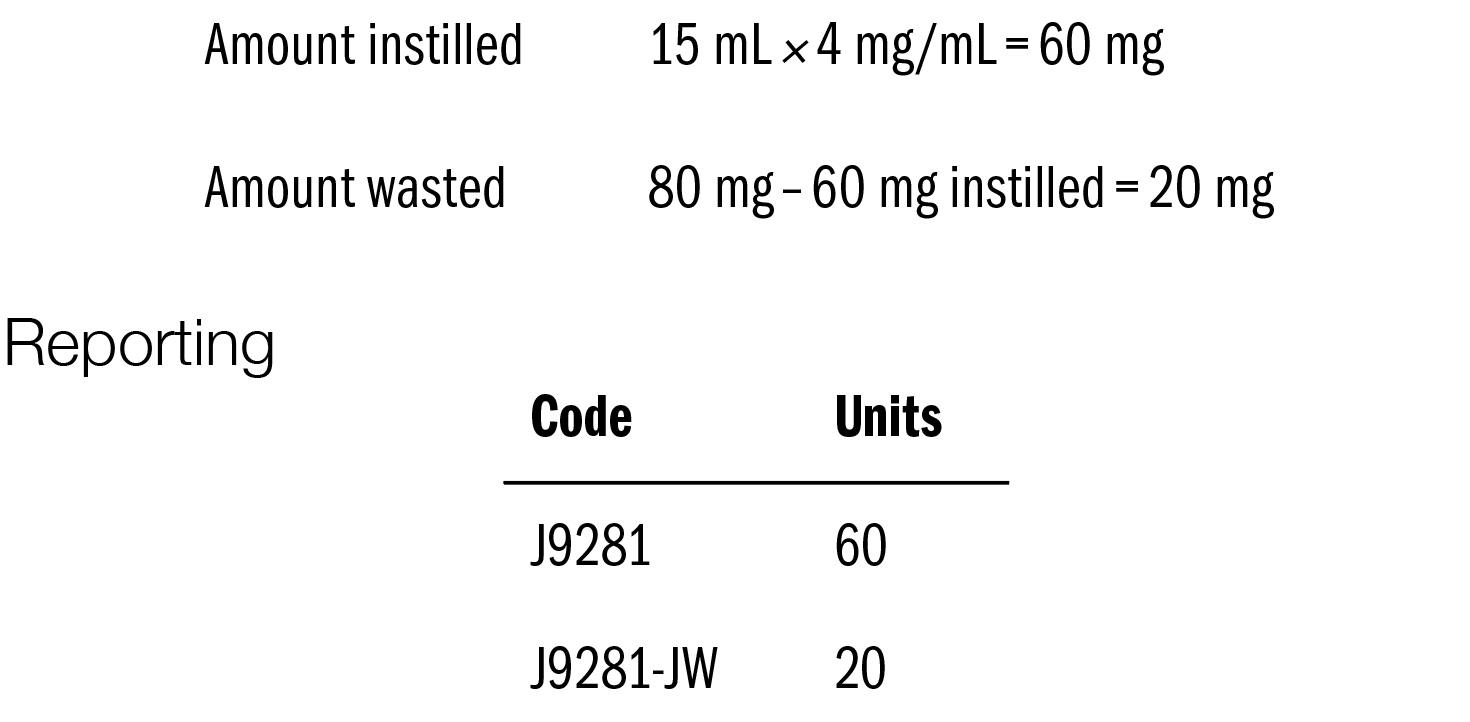
IMPORTANT: The total amount reported for each case is 80 mg; however, it is important to document and report both the amount instilled in the patient and the amount discarded for each treatment. The amount instilled is reported separately from the amount that is not used (discarded). The total of the instilled amount and the discarded amount is 80 mg for each case.
For reporting, the amount instilled for each case must be converted to milligrams or units when billed. The simple calculation for conversion is
Number of mL × 4 mg/mL
The entity reporting the mitomycin for pyelocalyceal instillation reports code J9281 on 2 separate lines of the claim form. The initial line is reported with no modifier, and the units reported are the result of the calculation above (number of mL instilled × 4 mg/mL). The second line is used to report the amount wasted, and “-JW” is appended to code J9281. The number of units reported for J9281-JW is the result of 80 mg
minus the number of milligrams instilled.
As an example, we use the recommended dose of 60 mg.
The physician administering the drug reports the use 15 mL of mitomycin for pyelocalyceal instillation gel:
Coding for the ASC or HOPD
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services has established Healthcare Common Procedural Coding System code C9789 (Instillation of anti-neoplastic pharmacologic/biologic agent into renal pelvis, any method, including all imaging guidance, including volumetric measurement if performed) (Table 1). Code C9789 would be reported by the ASC or HOPD instead of the CPT code reported by the physician for the professional fee for administering the drug, regardless of the approach (retrograde or antegrade).
The ASC may also report code 77420, if provided (as noted earlier), because the status of the code under the Outpatient Prospective Payment System is Z2, and it is allowed if provided integral to the service provided on the same date.
The J code is reported by the HOPD or ASC as noted earlier.
Article Information
Published: December 13, 2024.
Conflict of Interest Disclosures: The authors have nothing to disclose.
Funding/Support: None.
Author Contributions: All authors contributed to drafting, reviewing, and revising the manuscript and the decision to submit the article for publication.
Data Availability Statement: No new data were generated for this article.